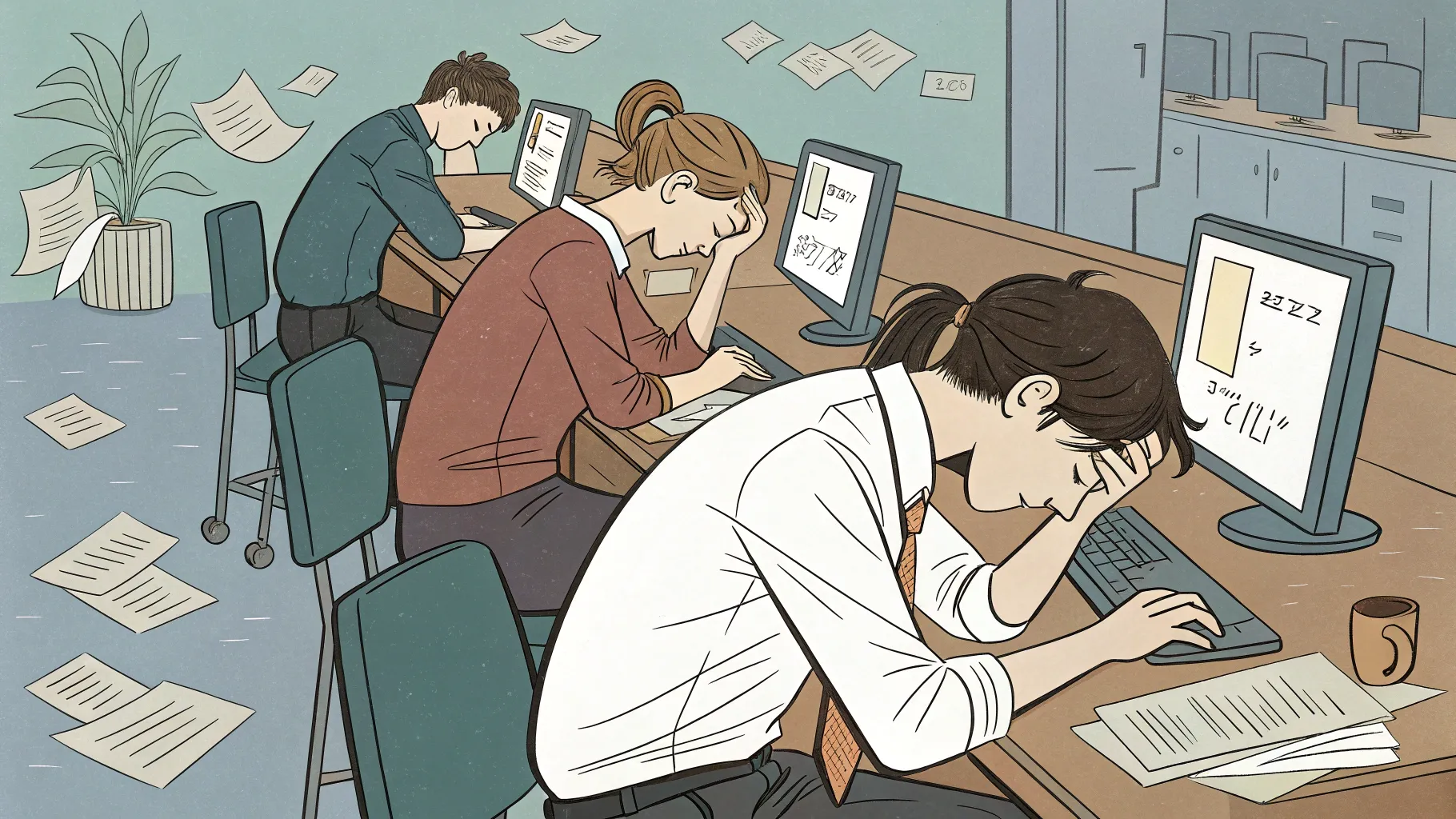

Recent research indicates that younger workers are approaching their limits of stress and burnout in today’s workplace environment. The findings suggest a growing crisis among the newest generations in the workforce, who are struggling to cope with professional demands and expectations.
The study reveals that many young professionals are experiencing unprecedented levels of workplace pressure, leading to concerns about long-term mental health impacts and potential workforce stability issues. This trend appears to be accelerating, with researchers noting significant increases in reported stress levels compared to previous years.
The Breaking Point Phenomenon
According to the research, younger employees—primarily Millennials and Gen Z workers—are reporting higher rates of exhaustion, disengagement, and dissatisfaction than their older colleagues. Many cite overwhelming workloads, blurred work-life boundaries, and economic pressures as key factors contributing to their distress.
“We’re seeing clear evidence that younger workers are hitting walls of endurance much earlier in their careers than previous generations,” notes the research. “This isn’t simply about being less resilient—it’s about facing a fundamentally different work landscape with new challenges.”
The data shows that nearly 60% of workers under 35 report feeling “maxed out” at least once per week, compared to 38% of workers over 45. These younger employees are also more likely to consider changing jobs due to stress-related concerns.
Factors Driving Young Worker Burnout
Several key elements appear to be fueling this crisis among younger workers:
- Economic pressure: Rising living costs combined with stagnant entry-level wages create financial stress
- Always-on culture: Digital connectivity that makes it difficult to disconnect from work
- Career uncertainty: Concerns about job security and career progression in volatile markets
- Higher expectations: Increased productivity demands in competitive work environments
The research also highlights that younger workers face unique challenges their predecessors didn’t encounter at the same career stage. Many entered the workforce during economic downturns, pandemic disruptions, or amid rapid technological change that constantly reshapes job requirements.
Workplace Responses and Solutions
Some forward-thinking organizations are already implementing changes to address these concerns. Flexible work arrangements, mental health resources, and revised workload expectations are among the most common interventions.
Companies that have adopted such measures report improvements in retention rates and productivity. One case highlighted in the research showed a 24% decrease in turnover after implementing a comprehensive wellness program targeted at younger employees.
“Organizations that recognize and respond to these warning signs are seeing significant benefits. Those that don’t are experiencing costly turnover and productivity losses,” the research states.
Human resource professionals are increasingly advocating for structural changes rather than simply offering stress management tools. This includes rethinking project timelines, communication expectations, and creating clearer boundaries between work and personal time.
The findings suggest that addressing this issue requires systemic changes rather than placing the burden on individual workers to develop better coping mechanisms. Without such changes, researchers warn that companies may face a talent crisis as younger workers seek alternatives that better support their wellbeing.
As this trend continues to develop, both employers and employees will need to find sustainable approaches to work that allow for productivity without pushing younger workers beyond their breaking points. The research concludes that the current trajectory is unsustainable and requires immediate attention from organizational leaders.










Howie Jones
My name is Howie and I'm a Customer Success Manager at Calendar. I like to ensure our customers get the best experience using our product. If you have questions email me howie at calendar.com